EASE 5 - Planning of immersive sound installations
Sound system installations for spatial audio and immersive sound continue to gain more and more presence in modern event venues. This also includes acoustic enhancement systems in case a room shall be kept acoustically flexible to be used for different applications. Within the last years, numerous manufacturers have developed highly sophisticated products and algorithms for such installations.
However, until the introduction of EASE 5, there has been no simulation tool available to support the planning of these types of installation. EASE 5 provides innovative features to help analyzing and predicting the performance of the immersive, spatial, or 3D sound systems. Loudspeaker coverage, loudspeaker density, localization of sources, content perception direction, and more acoustics characteristics are now under control with EASE. This enables engineers to better forecast the success of the design and the scale of the project, including cost and size of the system.
New design tools for immersive audio in EASE 5
Immersive sound generally aims to provide an excellent listening experience: It can create the most natural, or even an artificial acoustic environment for the audience.
This requires exact localizable reproduction of sources via loudspeakers spread around the audience, and the ability to pan these sources smoothly. In addition, the spatial impression of the room - such as the size - shall often be adjustable.
The key elements of such an installation are:
- Live sources such as instruments or speakers,
- Reproduction loudspeakers
- Microphones
- Signal processing, and
- Room geometry and acoustic materials.
EASE 5 supports all of these items in the simulation, except for special live sources and microphones. It can provide objective quantities for:
- Radiation of sources and the sound system by simulating direct SPL, coverage and localization
- Room acoustics by calculating RT, STI and other parameters
- Interaction of sources and the room by calculating Critical Distance, Clarity C50/C80, Lateral Fraction and other parameters.
In order to optimize the simulated sound system, EASE also provides controls for changing the input data into these calculations, such as loudspeaker orientation and the signal processing for the feed of the loudspeakers, as well as internal filters. Related to the room itself, the wall absorption can be customized.
Extended analysis of loudspeaker coverage
One of the new features implemented in EASE 5 is focused on improved analysis of loudspeaker coverage.
The coverage can be simulated and viewed in direct SPL mappings and the cumulative distribution chart, including threshold and mean values for the top 90% of the covered area.
In addition, the loudspeaker density mapping provides a clear view of which and how many loudspeakers contribute to the sound received at each listening location:
- A maximum level deviation of 3 dB among the included loudspeakers guarantees best conditions for an even coverage, which in turn allows panning with smooth localization. Alternatively, a greater tolerance of 6 dB can be selected as a criterion as well.
- A maximum level deviation of 10 dB would be suitable for enhancing the diffuse sound field and thus adjusting the perceived size of the room and the reverberation time.
Spatial localization analysis
Spatial localization analysis can be conducted by having a look at the arrival times and levels of the signals reproduced by the loudspeakers. Another new feature of EASE 5, the horizontal angle mapping, shows the direction from which the localized loudspeaker signal is perceived. Based on precedence curves, loudspeakers can be tuned by adjusting their gains and delays to be received as a localized source or to serve as support for the main system.
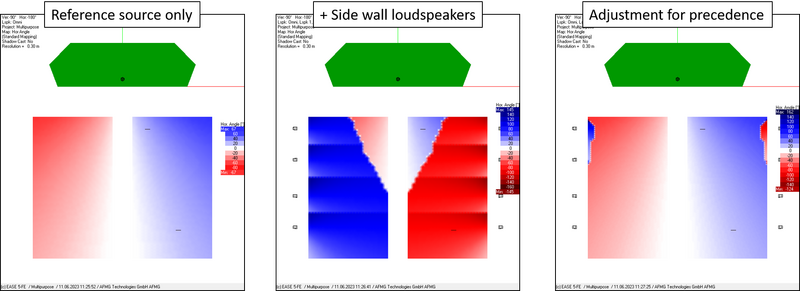
With the recently implemented innovative tools in combination with the high accessibility and usability of a modern software, EASE 5 takes the first step to help taking on immersive sound projects. Further steps are planned for the future.
Don't miss out our related paper "Validation and optimization of immersive sound reinforcement concepts using acoustic simulation tools" presented at the DAGA conference in Hannover in 2024 (German language).


